Digitalisation and Sustainability: Facts and Figures

According to the Greenpeace study, if employees in Germany worked from home one day a week, thanks to digital technologies and applications, at least 1.6 million tonnes of CO2 could be saved per year, and commuter traffic could be reduced by about 10.9 billion passenger kilometres.
According to the University of Freiburg, in comparison to traditionally held events, digital video conferences save up to 99.5% CO2.

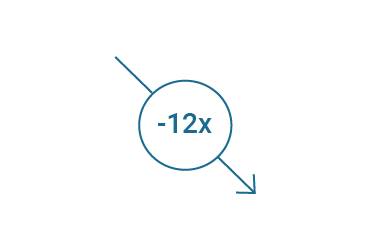
The CO2 emissions of European data centres have been on the decline since 2015. Today, they require 12 times less energy per workload than in 2010.
Through the consistent utilisation of waste heat from data centres, all residential and office space in Frankfurt – home to the world’s largest Internet Exchange – could be heated in a CO2-neutral manner by 2030.

As a general rule, switching to professional cloud computing providers saves companies up to 80 percent electricity compared to independently operated local infrastructure..
The 5G mobile communication standard transmits the same amount of data with almost 80 percent less energy than its 4G predecessor. Data transmission via fibre optic cables requires around 5 times less energy than copper connections.

According to the German Economic Institute, the manufacturing sector alone could save up to 10 billion Euro through the leverage effect of digitalization, and at the same time sustainably conserve resources.
The eco-balance of digitalisation is decidedly positive
