The Mission
The Internet is the foundation for Germany as a functioning business location and for an open and free society. The Internet industry is the key sector and growth engine of our time: its share of the overall economy has been rising continuously for years.
However, while providers and major social platform providers are often the focus of policymakers and the public, the companies that are at the beginning of the Internet value chain – namely operators of digital infrastructures such as data centres or colocation providers – and their achievements and challenges remain largely unknown. Nevertheless, this industry is of outstanding importance for a successful digital transformation in Germany.
A guarantee for the future viability of the location
Operators of digital infrastructures play a major role in ensuring the digital performance and economic future viability of Germany as a business location. The industry serves as a growth engine, a driver of innovation and a multiplier for other sectors (especially in the area of Industry 4.0), as well as a guarantor of tax revenues and employment.

In order to raise awareness of the importance of digital infrastructures in Germany and to engage in a constructive dialogue with policymakers, leading companies from various sectors of digital infrastructures – such as data centre operators, colocation providers, Internet service providers, carriers, cloud providers, software manufacturers and representatives from the application industry – have now joined forces under the umbrella of eco – Association of the Internet Industry to form an Alliance for the Strengthening of Digital Infrastructures in Germany.
As the largest European association of the Internet industry, eco represents over 1,000 member companies and has been committed to a forward-looking Internet policy and constructive exchange between policymakers and business for more than 30 years.

Energy-efficient data centres: Benefits for everyone
German data centres are among the most energy-efficient in the world – but there is still room for improvement. Investing in improved energy efficiency has two-fold benefits: lower energy consumption not only reduces CO₂ emissions, but also lowers operating costs.
Digitalisation & Sustainability: Facts and Figures

According to a Greenpeace study, at least 1.6 million tons of CO₂ per year could be saved in Germany, and commuter traffic could be reduced by approximately 10.9 billion passenger kilometres if employees – thanks to digital technologies and applications – worked from home one day a week.

According to the University of Freiburg, digital video conferences can save up to 99.5 per cent of CO₂ compared to in-person events.
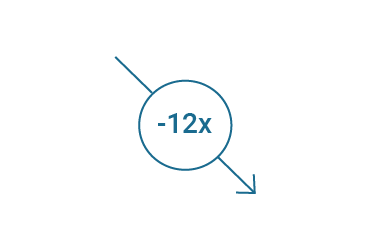
The CO₂ emissions of European data centres have been decreasing since 2015. Today, they now require 12 times less energy per workload than in 2010.
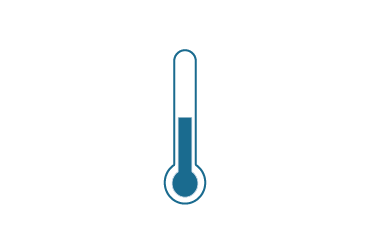
Consistent use of waste heat from data centres in Frankfurt – the location of the world’s largest Internet Exchange – would be enough to heat all the homes and offices in the city CO₂-neutrally by 2030.

In general, switching to professional cloud computing providers can save companies up to 80 per cent on electricity compared to independently operated local infrastructure.
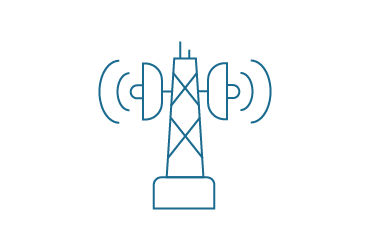
The 5G mobile communications standard transmits the same amount of data with almost 80 per cent less energy than its predecessor, 4G. Data transmission via fibre optic cable requires around five times less energy compared to copper connections.

According to the German Economic Institute, the manufacturing industry alone could save up to 10 billion Euro through the leverage effect of digitalisation, while simultaneously achieving sustainable resource conservation.
Six theses on the sustainability potential of digital infrastructures
- Digital infrastructures are part of the solution for achieving the climate goals: Data centres, broadband access and 5G networks are a key prerequisite for ecologically sustainable digitalisation and make a significant contribution to achieving climate Germany’s and Europe’s climate goals.
- The migration from in-house server infrastructures to cloud solutions offers high potential for increasing energy and resource efficiency and thus improving climate protection.
- A faster, politically controlled phase-out of coal in Germany, and a simultaneous accelerated expansion of renewable energies in power generation – for example, through so-called Power Purchase Agreements (PPAs) – will lead to a much stronger and, above all, faster reduction in CO₂ emissions via digital infrastructures.
- Artificial intelligence is enabling new and efficient product development, production processes and services that will contribute to the sustainable development of individual value chains or entire industries.
- Increasing digitalisation is accelerating the need for data centre capacities. The highest sustainability potentials are offered by an intelligent and sustainable combination of city and spatial planning as well as energy and data networks – in both urban and rural areas.
- Data centres offer a valuable source of heat. If the necessary political, societal and economic framework conditions for the utilisation of waste heat are created, data centres in this country can contribute more than 10 terawatt hours per year to Germany’s heating needs.

